金沢大学 環日本海域環境研究センター 臨海実験施設 http://rinkai.w3.kanazawa-u.ac.jp/
a) 超音波の細胞機能制御に関する研究
超音波は20 kHzを超える周波数の粗密波で,超音波探査や洗浄等,我々の身の回りに幅広く利用されています.また,超音波は医療分野において,診断に必須の技術であるのみならず,癌温熱療法,結石破壊,白内障の手術,血栓溶解,骨折治療等,治療にも利用されています.
低出力パルス超音波 (LIPUS) が骨折治療に有用なことは良く知られていますが,その分子メカニズムは依然不明な点が多いです.我々は,LIPUSをマウス前骨芽細胞様細胞MC3T3-E1に照射し,マイクロアレイを用いてLIPUSに応答する遺伝子群と遺伝子ネットワークを明らかにしました (1).これは単一の細胞から得られた成績であり,生体におけるLIPUSの効果をより正確に理解するためには,複数の細胞からなる組織やモデル動物で評価することも重要です.魚類のウロコには,ほ乳類の骨と同様に骨芽細胞と破骨細胞が存在し,骨の機能を評価する有用なモデルであることが知られています (2).LIPUSをウロコモデルに作用させた時,骨芽細胞が活性化し,破骨細胞にアポトーシスを誘導するという成績が得られています (3-5).今後,細胞,組織(ウロコモデルを含む)と動物モデルを用いて,超音波の細胞機能制御に関する研究を行いたいと考えています.
関連論文:
1) Tabuchi Y et al. Genes responsive to low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Nov 18;14(11):22721-40. PMID: 24252911
2) Suzuki N, Hattori A. Melatonin suppresses osteoclastic and osteoblastic activities in the scales of goldfish. J Pineal Res. 2002 Nov;33(4):253-8. PMID: 12390509
3) Kitamura K et al. Osteoblast activity in the goldfish scale responds sensitively to mechanical stress. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2010 Jul;156(3):357-63. PMID: 20223292
4) Kitamura K et al. Zebrafish scales respond differently to in vitro dynamic and static acceleration: analysis of interaction between osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2013 Sep;166(1):74-80. PMID: 23632157
5) Suzuki N et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound induces apoptosis in osteoclasts: Fish scales are a suitable model for the analysis of bone metabolism by ultrasound. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2016 May;195:26-31. PMID: 26850473
b) ストレス関連タンパク質の機能解析に関する研究
生体は,外界からの様々な刺激に対して巧妙な防御システムを備え,生体機能の恒常性を維持しています.例えば,生体が熱に曝された時,細胞の中ではheat shock response (HSR) が起こり,直ちに転写因子heat shock transcription factor 1 (HSF1) が活性化され,heat shock proteins (HSPs) が発現します.Hsp70等のHSPsは,シャペロン機能を有し,熱によるタンパク質の変性を回復させ,細胞の機能を維持します.HSF1とHSP関連タンパク質の細胞機能における役割やそれらとがんとの関連性に注目しています (1-5).
関連論文と総説:
1) Tabuchi Y, Kondo T. Targeting heat shock transcription factor 1 for novel hyperthermia therapy (review). Int J Mol Med. 2013 Jul;32(1):3-8. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1367. Review. PMID: 23636216
2) Yunoki T et al. The combination of silencing BAG3 and inhibition of the JNK pathway enhances hyperthermia sensitivity in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2013 Jul 10;335(1):52-7. PMID: 23395971
3) Tabuchi Y et al. Common gene expression patterns responsive to mild temperature hyperthermia in normal human fibroblastic cells. Int J Hyperthermia. 2013;29(1):38-50. PMID: 23311377
4) Yunoki T et al. BAG3 protects against hyperthermic stress by modulating NF-κB and ERK activities in human retinoblastoma cells. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015 Mar;253(3):399-407.
5) Yunoki T et al. Network analysis of genes involved in the enhancement of hyperthermia sensitivity by the knockdown of BAG3 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 2016 Jul;38(1):236-42. PMID: 27245201
神戸大学大学院 農学研究科 応用動物学講座 動物分子形態学分野
http://morfunc.main.jp/
c) 環境化学物質が生体に及ぼす影響に関する研究
私たちの身の回りには数え切れないほどの環境化学物質が存在し、現代の便利な生活を支えています。しかし、一部の環境化学物質は、私たちの体内に入ると化学的ストレス要因となり、健康に予期せぬ影響を及ぼすことがあります。我々は実験動物や培養細胞を用いて、「環境化学物質がどのように生体に影響するのか?」や「どのように未知の影響を予測・評価すればいいのか?」に着目した研究を行っています。
新たな環境化学物質の一例として挙げられるネオニコチノイド系農薬は、害虫のみに作用するとされ、現在国内で最も多く使用される農薬成分の1種です。我々はマウスを用いた実験により、本農薬が哺乳類の生殖機能や神経機能にも予想外の影響を及ぼすことを明らかにしてきました(1-5)。今後、これらの影響メカニズムを解明することで、私たちヒトへの影響予測やリスク評価に繋がる研究成果を発信することを目指しています。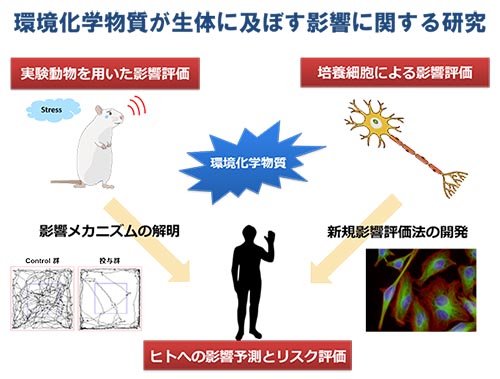
関連論文:
1) Hirano T, Yanai S, Takada T, …, Hoshi N. NOAEL-dose of a neonicotinoid pesticide, clothianidin, acutely induce anxiety-related behavior with human-audible vocalizations in male mice in a novel environment. Toxicol Lett. 2018. 282: 57-63.
2) Takada T, Yoneda N, Hirano T, …, Hoshi N. Verification of the causal relationship between subchronic exposures to dinotefuran and depression-related phenotype in juvenile mice. J Vet Med Sci. 2018. 80: 720-724.
3) Yoneda N, Takada T, Hirano T, …, Hoshi N. Peripubertal exposure to the neonicotinoid pesticide dinotefuran affects dopaminergic neurons and causes hyperactivity in male mice. J Vet Med Sci. 2018. 80: 634-637.
4) Yanai S, Hirano T, Omotehara T, …, Hoshi N. Prenatal and early postnatal NOAEL-dose clothianidin exposure leads to a reduction of germ cells in juvenile male mice. J Vet Med Sci. 2017. 79: 1196-1203.
5) Hirano T, Yanai S, Omotehara T, …, Hoshi N. The combined effect of clothianidin and environmental stress on the behavioral and reproductive function in male mice. J Vet Med Sci 2015. 77: 1207-1215.